Introduction
The exploration of space has always fascinated humankind. Over the years, we have ventured beyond the confines of our home planet, Earth, to explore the moon and various celestial bodies. However, the ultimate frontier of space exploration lies in the colonization of other planets. Mars, our neighboring planet, has emerged as a prime candidate for future human settlement. In this article, we will delve into the future of space exploration, focusing on the prospects of Mars colonization.
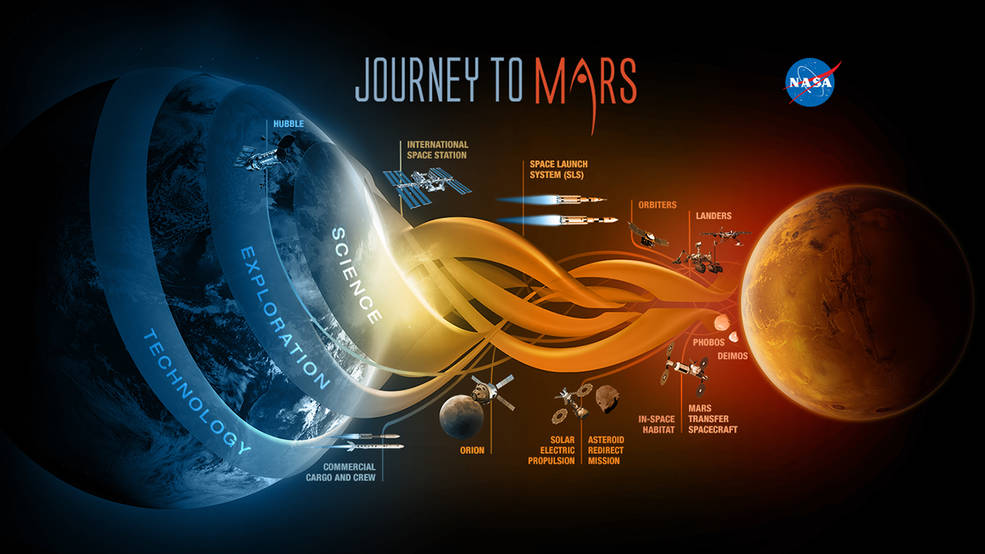
The Red Planet: Mars
Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet,” has captivated scientists and astronomers for centuries. Its proximity to Earth and relatively similar conditions make it an ideal target for human colonization. Mars is characterized by its dusty, barren landscapes, polar ice caps, and a thin atmosphere composed mostly of carbon dioxide. Despite these challenges, scientists believe that Mars holds the key to unlocking the mysteries of our universe and expanding the horizons of human civilization.
Advancements in Technology
The prospect of Mars colonization has become more realistic with advancements in technology. Space agencies and private companies have been actively working on developing the necessary infrastructure and spacecraft to facilitate human travel and settlement on Mars. One such notable project is SpaceX’s Starship, a next-generation spacecraft designed for long-duration space travel and the colonization of Mars. With ongoing research and development, technological breakthroughs are bringing us closer to the possibility of Mars colonization.
Challenges of Mars Colonization
Colonizing Mars comes with a myriad of challenges that must be overcome. Some of the main challenges include:
1. Distance and Travel Duration
Mars is located at an average distance of about 225 million kilometers from Earth. The journey to Mars can take anywhere from several months to over a year, depending on the alignment of the planets. The long travel duration poses significant physical and psychological challenges for astronauts, including exposure to radiation, muscle and bone loss, and isolation.
2. Harsh Environment
Mars has a harsh environment, with extreme temperatures, thin atmosphere, and high levels of radiation. The average temperature on Mars is around -63 degrees Celsius, and the lack of a protective magnetosphere exposes the surface to harmful solar radiation. Building habitats that can shield astronauts from these conditions is a critical challenge.
3. Life Support Systems
Maintaining life support systems is vital for the survival of humans on Mars. The planet lacks a breathable atmosphere and essential resources such as water and food. Developing sustainable systems for generating oxygen, growing crops, recycling waste, and managing limited resources is crucial for long-term habitation.
4. Psychological and Social Considerations
Mars colonization will require astronauts to spend extended periods in isolation and confined spaces. Psychological and social factors, such as crew cohesion, mental health, and communication with Earth, need to be carefully addressed to ensure the well-being and productivity of the colonists.
5. Cost and Sustainability
Mars colonization is an ambitious endeavor that requires significant financial resources. The cost of developing and launching the necessary infrastructure, as well as maintaining a sustainable presence on Mars, poses a considerable challenge. Finding ways to make the mission cost-effective and sustainable in the long run is crucial.
FAQs about Mars Colonization
1. Can Mars support human life?
Mars currently lacks the necessary conditions to support human life as we know it. However, with the development of advanced technology and infrastructure, it may be possible to create habitable environments and sustain human life on Mars in the future.
2. How long would it take to colonize Mars?
The timeline for Mars colonization is still uncertain. It depends on various factors, including technological advancements, funding availability, and international collaborations. Estimates range from a few decades to several generations.
3. What are the potential benefits of Mars colonization?
Mars colonization offers numerous potential benefits. It could serve as a stepping stone for further space exploration, provide new scientific discoveries, stimulate technological advancements, and offer opportunities for resource extraction.
4. Will Mars colonization solve overpopulation on Earth?
While Mars colonization may provide an additional living space for humans, it is unlikely to solve the issue of overpopulation on Earth. The challenges and limitations of living on Mars make it an impractical solution for addressing population growth on our home planet.
5. Are there any ethical concerns regarding Mars colonization?
Mars colonization raises ethical considerations, such as the potential disruption of Martian ecosystems, the rights of indigenous microbial life, and the equitable distribution of resources and opportunities among nations. These concerns must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible and sustainable colonization efforts.
6. Will Mars colonization be a one-way trip?
Initial Mars missions may involve one-way trips, with colonists committing to a permanent settlement. However, as technology and infrastructure improve, there may be possibilities for two-way travel and increased mobility between Mars and Earth.
Conclusion
Mars colonization represents a bold and exciting vision for the future of space exploration. While numerous challenges exist, advancements in technology, scientific research, and international collaborations are paving the way for humanity’s eventual journey to the Red Planet. Overcoming the obstacles of distance, harsh environment, life support, psychology, and sustainability will require collective efforts and perseverance. As we venture towards Mars, we embark on a new chapter in human history—one that expands our understanding of the universe and pushes the boundaries of human potential.
============================================
